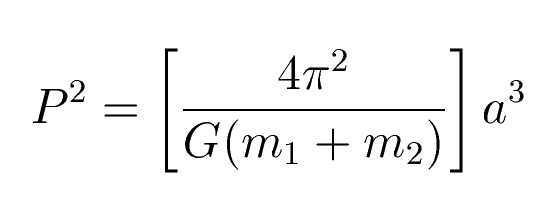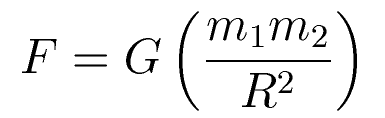Review
Printable
version
March
7, 2000
Announcements
General
Topics
-
Scientific
Method
-
Motion
of stars (rotation of Earth)
-
Seasons
(tilt, orbit of Earth)
-
Moon
phases and eclipses (orbit of moon)
-
Apparent
motion of planets
-
Planetary
orbits
-
Electromagnetic
radiation
-
Telescopes
-
9 planets,
7 major moons
-
Formation
of solar system
-
Earth:
geology
-
Earth:
atmosphere
-
Moon
Scientific
Method
-
Observation
-
Hypothesis
-
Test under all circumstances
(if possible)
-
Check for unexpected results
-
Group of correct hypothesis
= theory
-
If observation disagrees
with hypothesis, modify hypothesis
Motion
of Stars
-
Stars appear to move from
east to west every day (like this sun)
-
In reality, the Earth is
rotating west to east (counter clockwise)
-
Pattern of stars (constellations)
is essentially fixed
-
Different constellations
appear at different times of year
Seasons
-
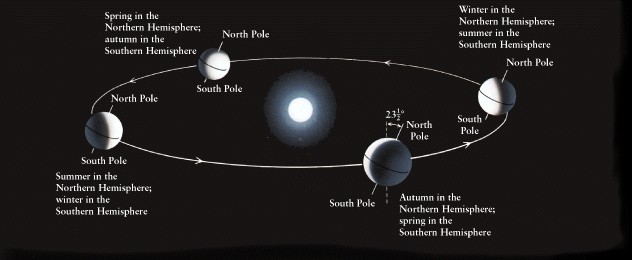
Primary cause of the seasons
is: 23.5o
tilt of the Earth's axis
-
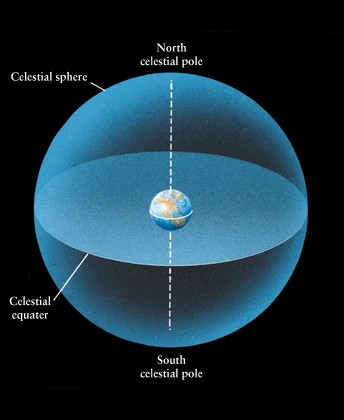
Celestial sphere defined
by rotation of earth
-
Ecliptic is path of sun
-
Equinox and solstice points
can be thought of as directions towards sun

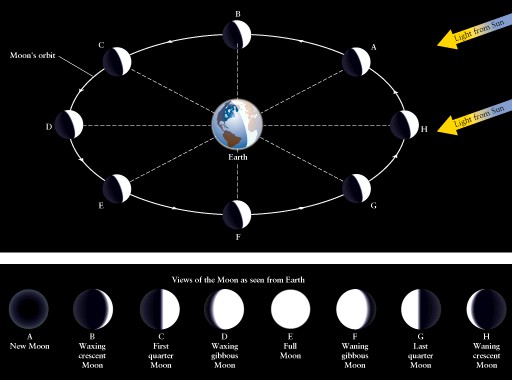
Orbit
of of Moon
-
Phases of moon: our view
of the sunward side of moon
-
Sidereal month (relative
to stars): 27.3 days
-
Synodic month (relative to
Sun-Earth line): 29.5 days
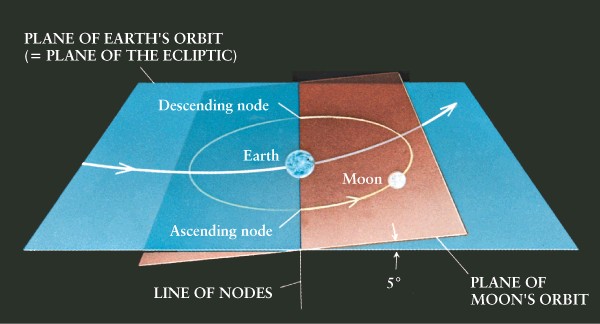
-
Solar eclipse: Sun is blocked
by moon
-
Lunar eclipse: moon is blocked
by earth
-
Tilt of moon's orbit is why
we don't have eclipses every month
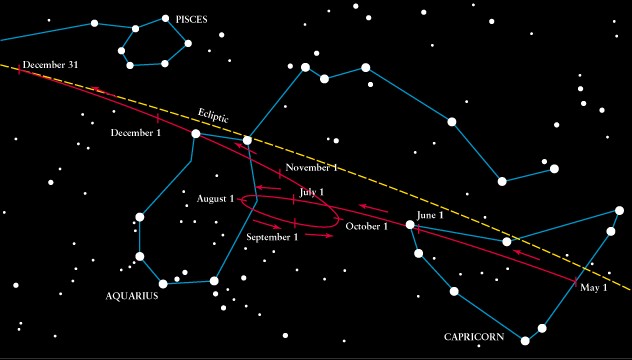
Apparent
motion of Planets
-
Planet means "wanderer" in
Greek
-
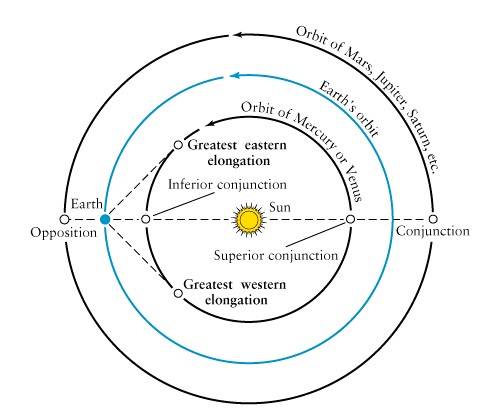
Most planet motion is west
to east like the sun (direct motion)
-
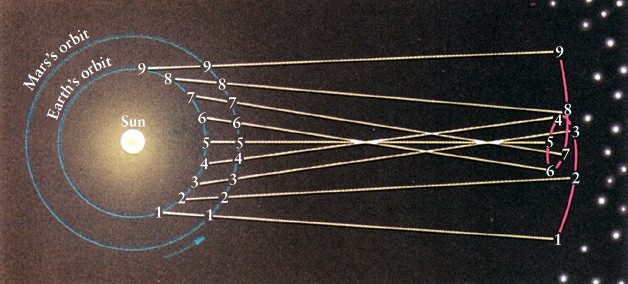
Superior planets an exhibit
retrograde
motion
-
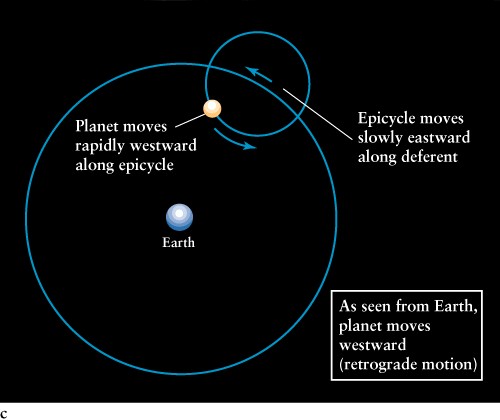
Ptolemy (Greek astronomer)
invented deferent/epicycle system to explain retrograde motion
-
Really, we are overtaking
the planet in its orbit
Planetary
orbits
-
Kepler figured out the answer,
Newton added understanding
-
Kepler's 3 laws:
-
1) Planets orbit Sun in an
ellipse with the Sun at one focus
-
2) A line joining the planet
to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time
-
3) P2 = a3
(Period in years, semi major axis in AU)
-
Newton's form of Kepler's
3d law:
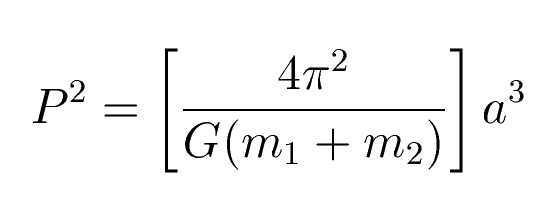
-
Newton's laws of motion:
-
1) A body at rest remains
at rest, a body in motion remains in motion with a constant velocity (same
direction and speed) unless acted on by a net outside force
-
2) F = ma
-
3) For every action (force),
there is an equal and opposite reaction
-
Newton's Universal law of
gravitation (the apple thing):
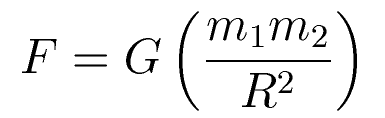
Electromagnetic
Radiation
-
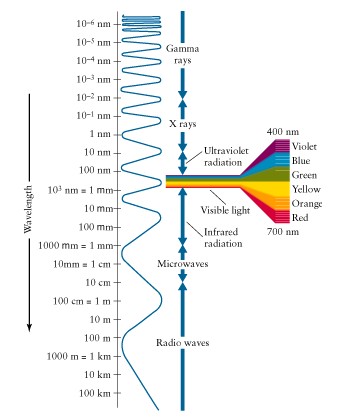
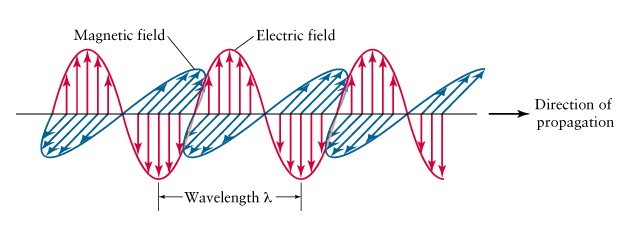
Visible
light, radio waves, X-rays, (see fig) all electromagnetic (EM) radiation
-
Absolute
speed limit of EM radiation:
-
Wavelength
(l)
and
frequency (n) related
-
Energy
and frequency related (think
of sneezing).
-
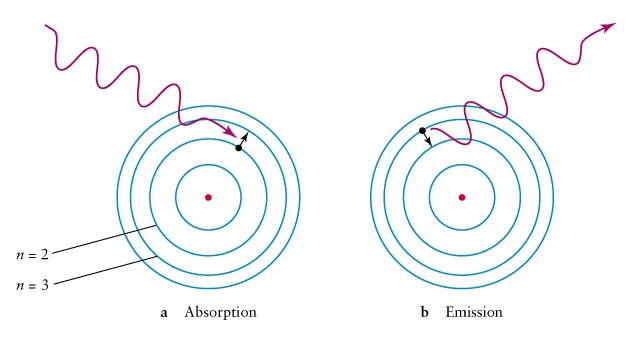
Spectral
lines caused by electrons jumping between energy levels

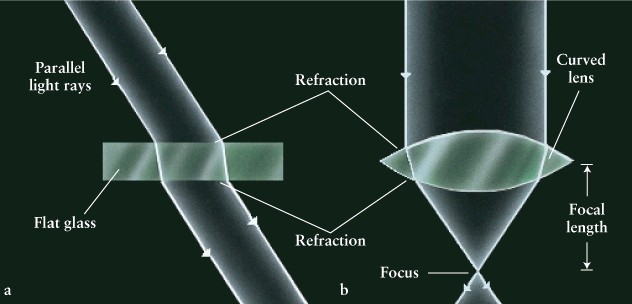
Telescopes
-
Refracting
(lenses)
-
Reflecting
(mirrors)



9
Planets 7 major moons
-
Terrestrial
-
Jovian
-
Jupiter
-
Saturn
-
Uranus
-
Neptune
-
Other: Pluto
-
Galilee moons of Jupiter:
-
Io
-
Europa
-
Ganymede
-
Callisto
-
Our moon
-
Titan (Saturn)
-
Triton (Neptune)


Formation
of Solar System
-
Solar system formed from
a nebula (cloud of gas)
-
Nebula, like the Universe
is mostly hydrogen and helium
-
Solar nebula enriched with
heavier elements formed in the centers of stars and released in supernova
explosions (star barf)


Earth:
geology
-
Earth's surface is 3/4 water
-
Rocks are made up of minerals
-
Minerals are (combinations
of) elements
-
Types of rocks
-
Igneous -- cooled magma/lava
-
Sedimentary -- old lake/sea
bottom
-
Metamorphic -- squished
-
Use seismic waves (earthquakes)
to study earth's layered structure
-
Inner core (solid iron)
-
Outer core (liquid iron)
-
Mantle (solid jacket)
-
Crust (solid lighter elements
than iron)
-
Upper mantle is plastic (magma)
-
Convection in upper mantle
causes plates of crust to move
-
Plate tectonics causes earthquakes
-
Volcanos appear along plate
boundaries and in select hot spots (like Hawaii)


Earth:
atmosphere
-
Composition: 3/4 nitrogen,
1/4 oxygen
-
Four distinct regions
-
Troposphere -- where weather
occurs
-
Stratosphere -- ozone
layer
-
Mesosphere --
-
Thermosphere -- +80 km
-
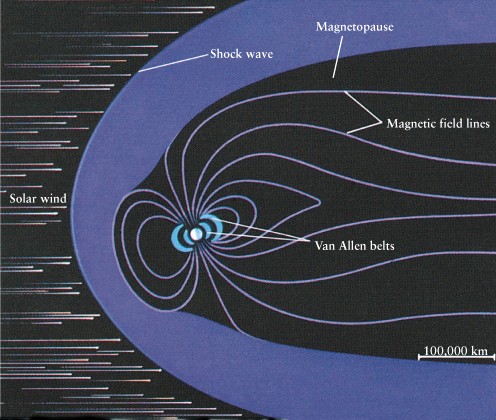
Magnetosphere -- solar wind
interaction with magnetosphere causes Northern Lights
Our
Moon
-
Cratered highlands
-
original surface
-
4.6 billion years old
-
Smoother Maria
-
lava filled craters
-
3.5 billion years old
-
Moon (and Sun) causes tides
-
Moon probably formed by collisional
ejection event