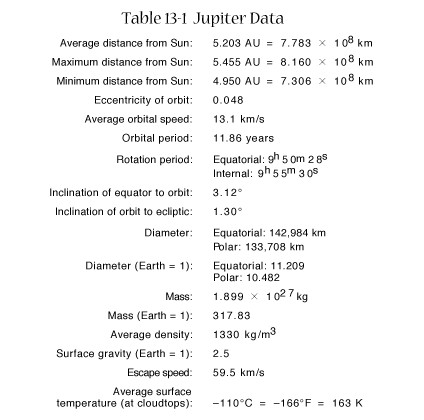
Jupiter
Printable
version
April
11, 2000
Announcements
-
Hand
in Homework 5
-
Quiz
#2 in discussion section this week
-
Covers
Chapters 18.1-18.6, 10,11,12
Jupiter
Preview
-
Jupiter
overview
-
Seeing
Jupiter from Earth
-
Jupiter's
composition
-
Cloud
top patterns
-
Outer
atmosphere dynamics
-
Comet
Shoemaker Levy 9 impact
-
Jupiter's
Magnetic field, magnetosphere
-
Spacecraft
visits
Jupiter
Overview
-
Superlative planet
-
Equatorial and polar rotation
rates different
-
Differential rotation (like
sun)
-
Inside and outside rotation
rates different
-
Equatorial and polar diameters
different (oblate)
-
Jovian planet (density is
lower than terrestrial)
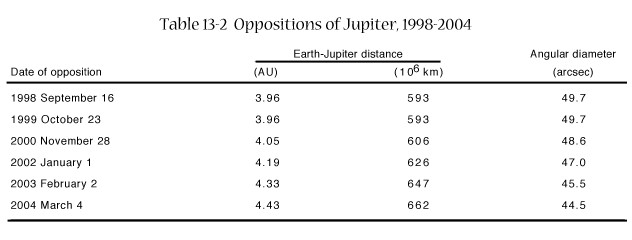
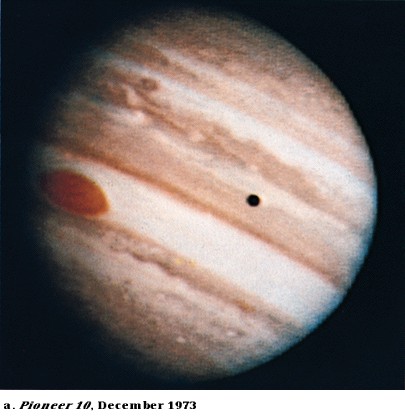
Seeing
Jupiter from Earth
-
Jupiter is a superior
planet (larger orbit)
-
Opposition every 13 months
-
One of the brightest objects
in the sky
-
Looks big in a telescope
-
Easy to see belts (dark)
and zones (light)
-
Easy to see red spot

Jupiter
Composition
-
Jupiter's average density
is 1330 kg/m3
-
Rock density is 3000 kg/m3
-
Jupiter can't have much rock
-
Jupiter is not round
-
oblate
-
equatorial diameter 6.5%
larger than polar diameter
-
Differential rotation: can't
be a solid body
-
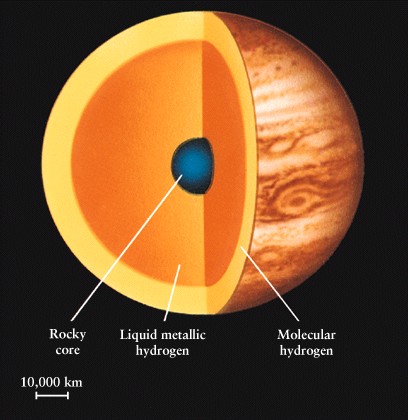
Jupiter has some rocky core
-
Saturn probably has a smaller
core
-
Jupiter is mostly gas
-
hydrogen and helium
in same proportions as Sun
-
formed at the same time as
the Sun
-
Weight of gas in central
regions is HUGE
-
rocky core may be compressed
to 20,000 kg/m3
-
80 million atmospheres
-
liquid metallic hydrogen
surrounds core
-
unusual conductive form of
hydrogen
-
caused by high pressure and
temperature
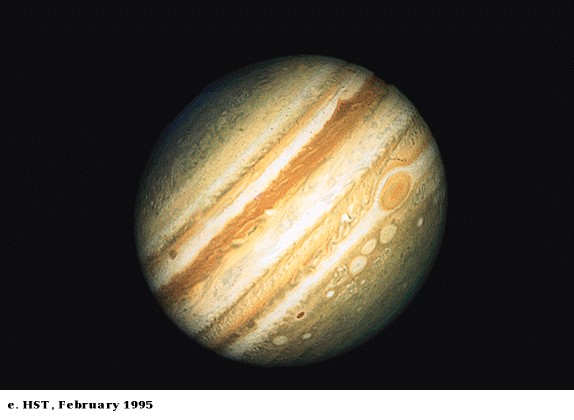
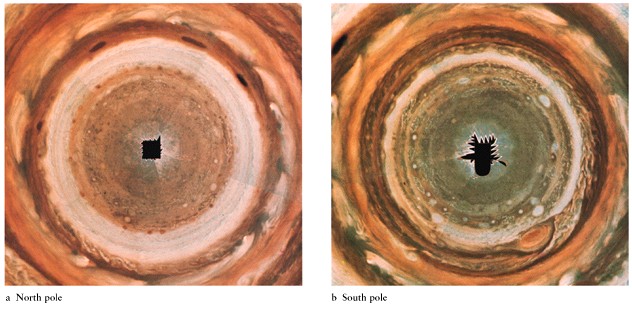
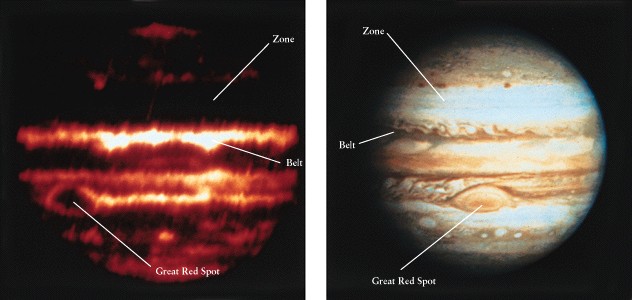
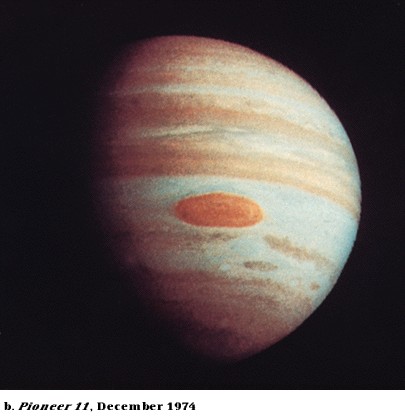
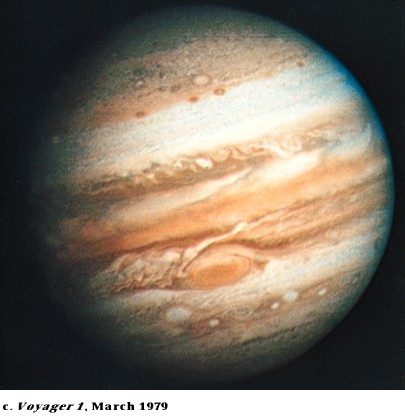
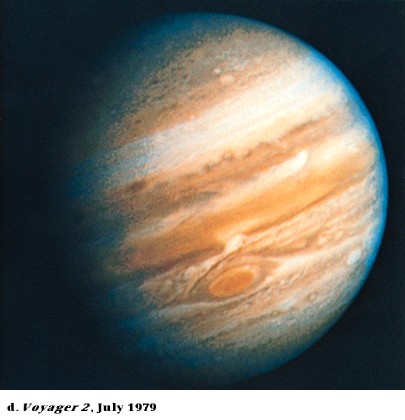
Cloud
Top Patterns
-
Belts (dark) and zones (light)
-
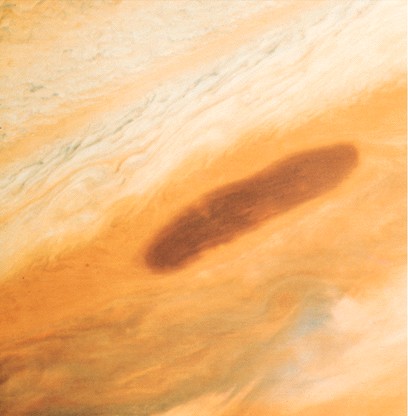
Great red spot
-
storm raging since at least
1664 when first seen by Robert Hooke
-
Changes size slightly, but
about as big as 3 Earths
-
white ovals (two recently
merged)
-
brown ovals
-
patterns are pretty similar
in northern and southern hemispheres
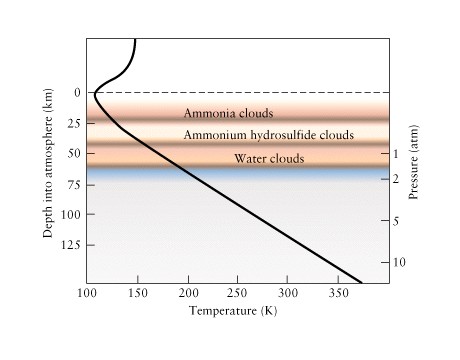
-
Clouds in 3 layers
-
Ammonium: NH3
-
Ammonium hydrosulfide: NH4SH
-
Water
-
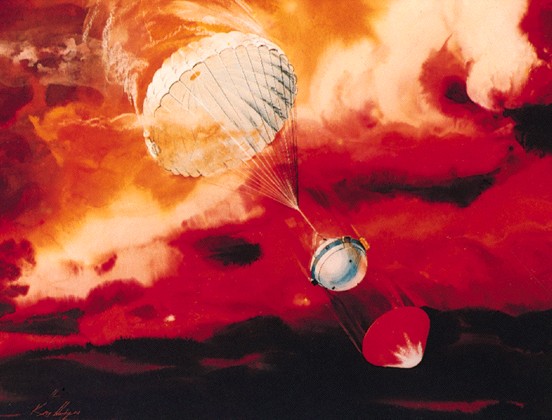
Galileo Probe
failed to detect water clouds
-
may have been a hole in the
water clouds
-
Mystery: what causes the
colors?

\

Outer
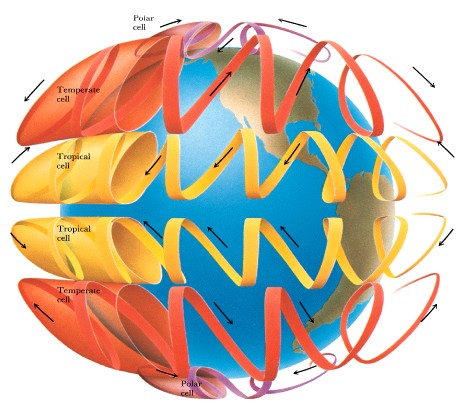
Atmospheric Dynamics
-
Jupiter produces ~2 times
as much heat than it receives from the Sun!
-
Probably residual heat from
formation
-
larger bodies cool more slowly
-
Jupiter rotates rapidly
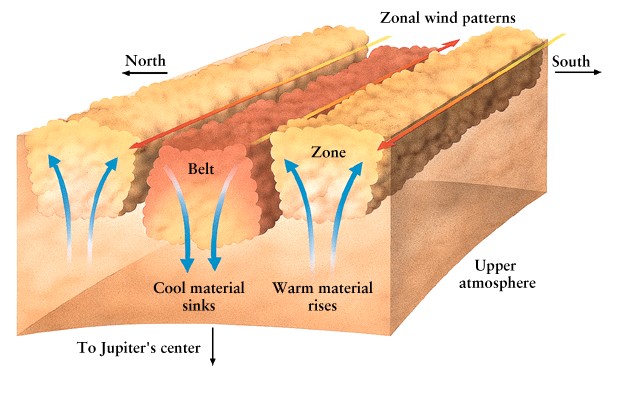
-
Convection cells broken by
rotation (like Earth)
-
Zones (light) upwelling
-
Belts (dark) downdraft
-
Fastest winds in belt/zone
boundary (500 km/hr)
-
Whitish clouds tend to be
high, cooler
-
Brown ovals are holes in
clouds, show warmer layers below
-
Exception: Great Red Spot
rises to high altitudes
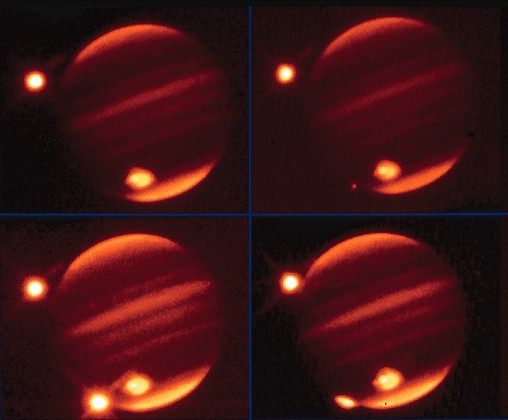
Comet
Shoemaker-Levy 9 Impact
-
Spectacular collision in
1994 between comet and Jupiter
-
Comet had been one piece
until previous pass by Jupiter
-
broke into more than 20 pieces
-
Pieces hit Jupiter one by
one
-
Left scars that healed up
after a few weeks



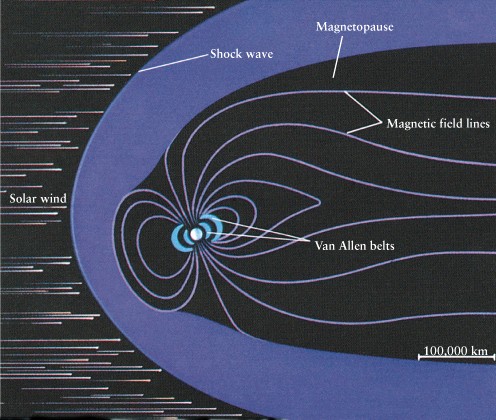
Jupiter's
Magnetic Field/Magnetosphere
-
Generated
by circulating charges in liquid metallic hydrogen core
-
analogy
to circulating charges in Earth's liquid iron core
-
Jupiter's
field is more than 10 times stronger than Earth's
-
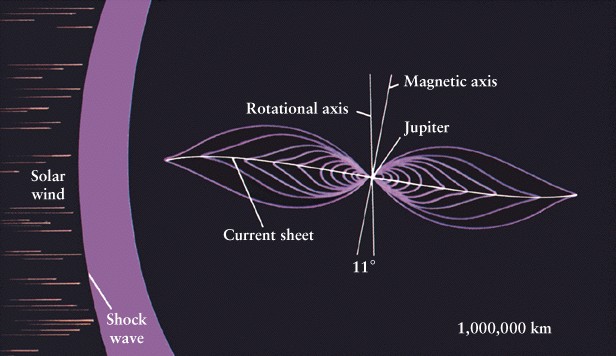
Jupiter's
magnetic field tilted 11 degrees with respect to Jupiter's rotation axis,
rotates slower than atmosphere
-
Equatorial:
9h 50m
-
Magnetic
field: 9h 55m
-
Carves
out magnetosphere in solar wind
-
Recall
Earth's magnetosphere caused Aurora Borealis (Northern lights)
-
Charge
stored in van Allen Belts
-
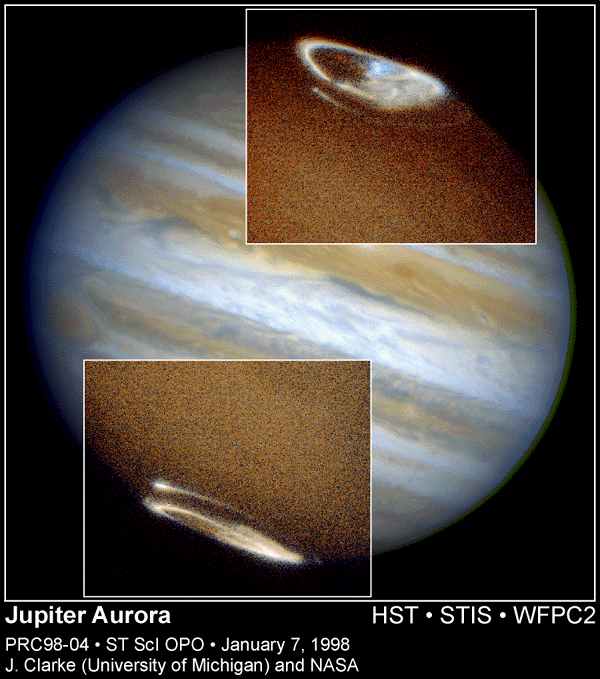
Jupiter
has Aurora as well
-
Jupiter's
stored charges flung out by fast rotation into a current sheet
-
Visible
at radio wavelengths
-
electrons
spiral around magnetic field lines
-
oscillating
charges send out radio waves
Spacecraft
Visits
-
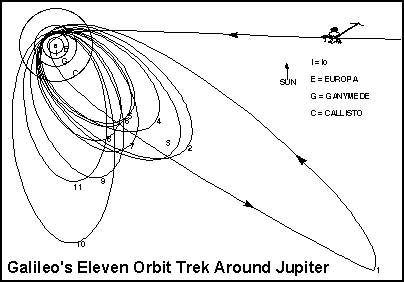
Flyby
-
Orbit
-
Galileo
1995--present
-
Sent
in atmosphere probe
-
Cassini




Galileo
composite image of Great Red Spot
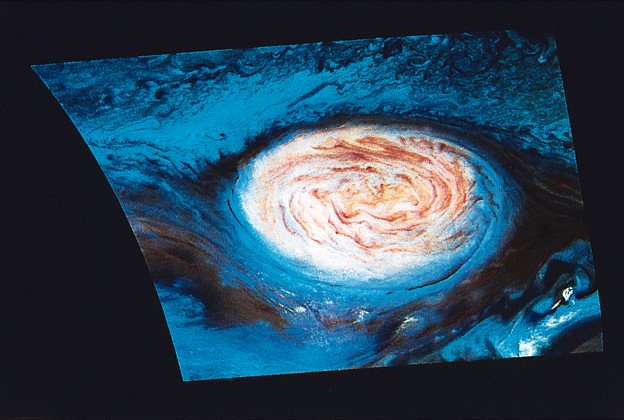

Jupiter
Summary
-
Jupiter
overview
-
Seeing
Jupiter from Earth
-
Jupiter's
composition
-
Cloud
top patterns
-
Outer
atmosphere dynamics
-
Comet
Shoemaker-Levy 9 impact
-
Jupiter's
Magnetic field, magnetosphere
Spacecraft
visits


























