Earth:
Geology
February
24, 2000
Announcements
-
HOMEWORK
#3
on web
-
Solutions
to homework #2 on web
-
QUIZ
THIS WEEK IN DISCUSSION SECTION
-
Covers
chapters 1-6
-
22
multiple choice test problems (similar to midterm/final)
-
1 longer
answer like homework (worth 3 multiple choice problems)
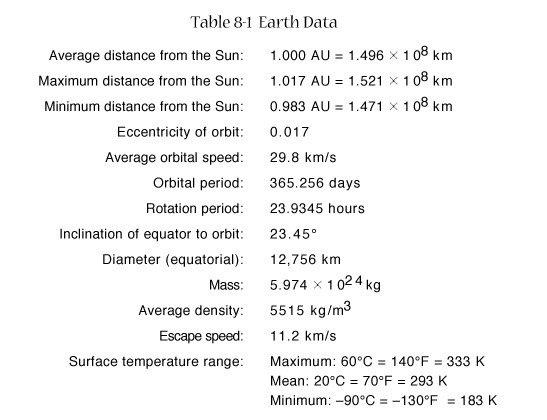
Basic
Earth Data
Surface
Properties
-
3/4 of Earth's surface covered
with water
-
average surface temperature
of 70o F
-
water is, on average, liquid
-
water probably came from
icy planetesimals
-
Land and sea beds composed
of rocks
-
Igneous -- cooled magma/lava
-
Sedimentary -- old lake/sea
bottom
-
Metamorphic -- squished
What
are Rocks Anyway?
-
Rocks are (combinations of)
minerals
-
Minerals are in turn composed
of one or more elements
-
single elements:
-
Gold -- gold
-
Diamond -- carbon
-
More than one element
-
Quartz -- silicon, oxygen
-
Feldspar -- silicon, aluminum,
oxygen
Quartz, Feldspar, Mica
Types
of Rocks
-
Igneous rocks
-
mineral soup
-
magma (under surface)
-
lava (above surface)
-
Basalt, Granite
-
Sedimentary rocks
-
mineral sandwiches
-
lake and ocean beds
-
Limestone, Sandstone (Wisconsin)
-
Metamorphic rocks
-
squished rock
-
rock becomes (re)buried,
high pressures and temperatures metamorphose the rock
-
Marble, Schist
Lava
Basalt, Granite
Limestone, Sandstone
Marble, Schist
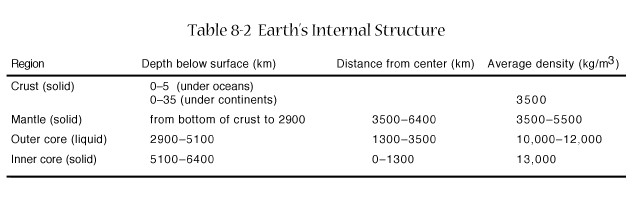
Journey
to the Center of the Earth
-
In hot protoplanet Earth,
heavy stuff like iron (Fe) sank
-
Lighter stuff like silicon,
aluminum and oxygen (Feldspar) floated
-
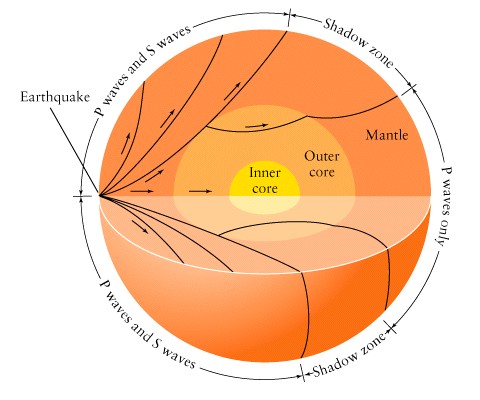
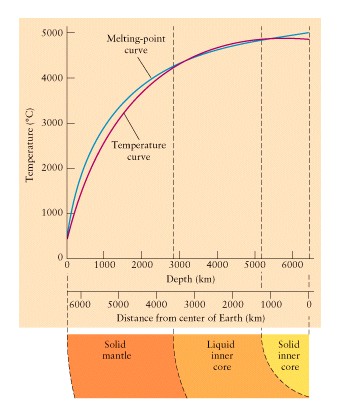
Earthquake studies reveal
layered structure of Earth's core
-
waves from earthquakes (seismic
waves) travel through the earth!
-
like refraction of light
in glass, these waves bend at sharp material boundaries
-
allow mapping of inner layers
-
we can't go there but seismic
waves can
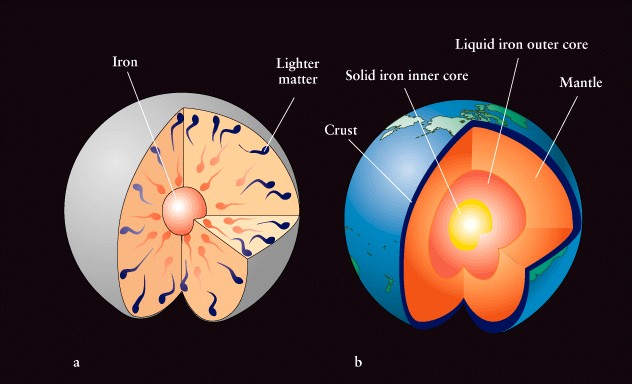
Types of waves from earthquakes
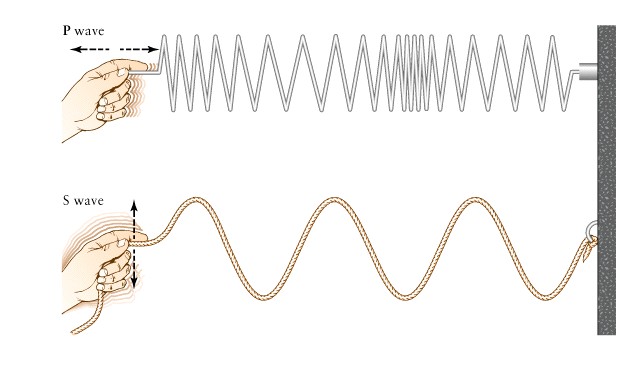
Onion
Earth
-
inner
core, outer core, mantle, crust
-
outer
mantle is plastic (flows slowly)
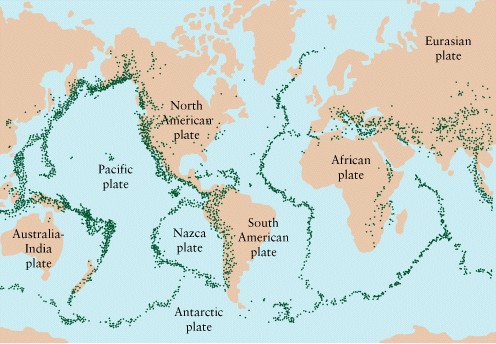
Plate
Tectonics
-
Sections of the crust move
relative to each other slowly
-
Evidence: similar rocks in
different places
-
Sensitive instruments can
measure yearly motion
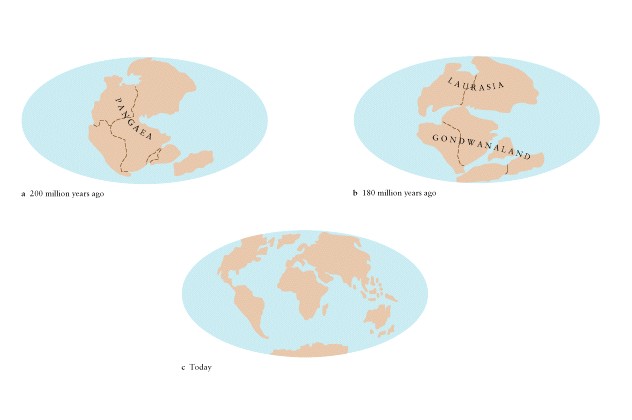
-
Pangaea 200 million years
ago
-
Laurasia, Gondwanaland 100
million years ago
-
Compare to age of Earth 4-5
billion years -- may have been earlier versions of Pangaea
Earthquakes
-
Earthquakes
are caused by plate tectonics
-
Plates
often stick when moving relative to each other
-
earthquake
happens when plates slip
-
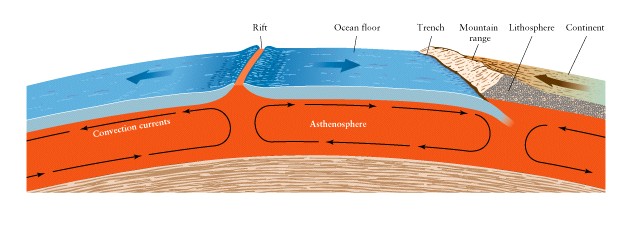
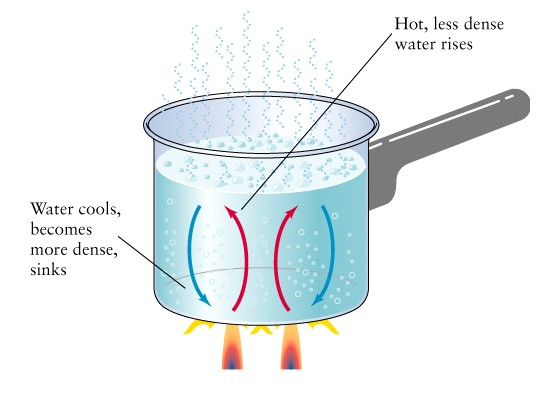
Plate
motion caused by convection in the Asthenosphere (soft upper mantle)
-
Plates
are part of the lithosphere
Hot
Spot Volcanism
-
Volcanos
happen where crust is thin
-
Plate
boundaries
-
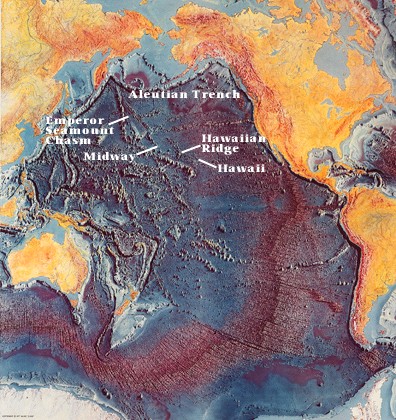
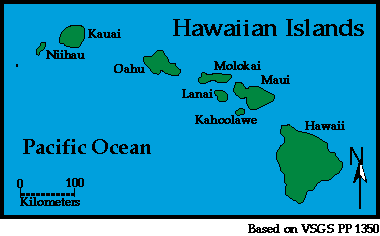
Hot
spots like Hawaii
-
Hawaii's
hot spot remains fixed, plate moves
-
Venus
and Mars have hot spot volcanism but no plate motion -- BIG volcanos
Geology
Summary
-
Earth's surface 75% water
-- different from other terrestrial planets
-
Rocks are mineral(s)
-
Igneous, Sedimentary, metamorphic
rocks
-
Earth: inner core, outer
core, mantle, crust
-
Crust divided into plates
-- unique among terrestrial planets
-
Plates move because of convection
in upper mantle
-
earthquakes
-
continental drift, Pangea
-
Volcanos -- hot spot volcanism












