Earth:
Atmosphere
Printable
version
February
29, 2000
Announcements
Preview:
Earth's Atmosphere
-
Composition
-
Structure
-
Effect
of Earth's magnetic field
-
Biosphere
Composition
of Atmosphere
-
Earth's atmosphere is mostly
Nitrogen
-
Relative to other planets
in solar system has lots of Oxygen
-
Oxygen comes from biological
processes
-
Photosynthesis in plants:
requires carbon dioxide (CO2), gives of Oxygen (O2)
-
Life on Earth for 3.8 billion
years (Earth is 4.5 billion years old)

Vertical
Structure of Atmosphere
-
General property of all planetary
atmospheres:
-
Each gas molecule attracted
by gravity
-
Gas molecules hit each other
-
Balance of forces determines
atmospheric
pressure
-
highest at surface
-
decreases smoothly as altitude
increases
-
On Earth, decreases by a
factor of 2 every 5500 m (18,000 ft)
-
Other planet atmospheres
have different scale heights
-
why
its hard to catch your breath at high altitude
-
why
planes are pressurized
Temperature
Structure of Atmosphere
-
Four distinct regions
-
Troposphere
-
Stratosphere
-
Mesosphere
-
Thermosphere

Troposphere
-
Troposphere heated by sun-warmed
ground
-
warm closest to ground/sea
level
-
heat from bottom causes convection
(lava lamp)
-
warmer at equator than poles
sets up preference for convection motion -- convection cell
-
Earth rotation breaks up
cells
slowly rotating Venus
has fewer cells

Stratosphere/Ozone
Layer
-
Ozone layer is in the Stratosphere
-
Stratosphere heated by absorption
of UV light from Sun by Ozone (O3)
-
UV light from "raw" sunlight
would give you a bad sunburn in 10 seconds!
-
Ozone layer very important
to life on Earth
-
Chloroflurocarbons (CFCs)
react with ozone and destroy it
-
CFCs used in refrigerators,
air conditioners
-
Ozone generated naturally
in Stratosphere by sunlight
-
We have dumped so much CFC
into the atmosphere that there is a hole in the ozone layer over antarctica!
-
CFCs are now being phased
out.
Temperature
vs altitude graph
Upper
Atmosphere
-
(Mesosphere)
-
Thermosphere
-
no upper limit
-
fades off into thin interplanetary
gas
-
UV radiation ionizes
the gas in the thermosphere
-
Ionosphere is first
300 km of thermosphere
-
AM and short-wave radio waves
bounce off of ionosphere
-
Ham radio operators talk
around the world
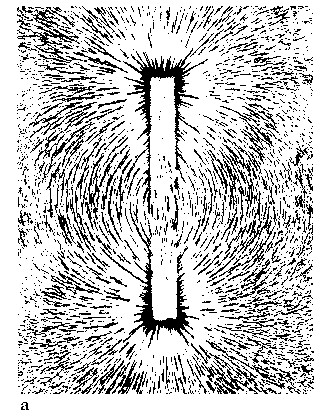
Production
of Earth's Magnetic Field
-
Caused
by moving electric charges in Earth's iron core
-
NOT
a big iron magnet at the center of the Earth
-
HOWEVER,
pattern of magnetic field is similar
-
Axis
of magnetic field differs from Earth's rotation axis
-
compass
needle points to magnetic north, not true north

Effect
of Earth's Magnetic Field
-
Moving
charges make magnetic fields
-
Magnetic
fields make charges move
-
Solar
wind composed of fast moving protons and electrons (400 km/s)
-
If
magnetic fields make charges move, why does the solar wind slow down when
it hits the Earth's magnetic field?
-
Resulting
cavity in solar wind called magnetosphere
-
Magnetopause
is balance point between magnetic field and solar wind
-
Some
solar wind charged particles leak through magnetopause
-
accumulate
in Van Allen belts
-
cause
Aurora Borealis (northern lights)
-
Aurora
Australis (southern lights)
-
Aurora
seen on Jupiter and Saturn
-
Aurora
formed when solar wind protons (directed by the Earth's magnetic field)
slam into the atmosphere
-
effect
is similar to neon light/spectrum tube



Biosphere
-
Home of all living creatures
on Earth
-
3 km deep in crust
-
10 km high in troposphere
-
Living creature's outputs
have impact on atmosphere
-
Plants create oxygen :-)
-
CFCs deplete ozone :-(
-
Industrial processes create
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
-
The greenhouse effect: Carbon
dioxide (CO2) helps trap heat by transmitting UV, reflecting
IR
-
CO2 content increasing
since 1958. What did it do before then?
-
Global warming?
-
These effects may not be
"real." Do you want to take the chance?
Atmospheric CO2
content measured in Hawaii

Average global temperature
temperature change

Review:
Earth's Atmosphere
-
Composition
-
Structure
-
Pressure drops factor of
2 every 5500 m (18,000 ft)
-
Layers by temperature
-
Convection in lowest layer
causes weather
-
Ozone in second layer
-
Effect of Earth's magnetic
field
-
interacts with solar wind
-
magnetosphere
-
Aurora Borealis (Northern
lights)
-
Biosphere
-
Living creatures have changed
the atmosphere for good and bad









