MARS
Printable
version
March
30, 2000
Announcements
-
Quiz
#2 in discussion section next week
-
Covers
Chapters 18.1-18.6, 10,11,12
-
Homework
5 due next Tuesday
-
Observing
project:
-
Daylight
savings time this past weekend
-
Next
Honors section:
-
THIS
Wed April 5 (weather permitting) at 8:00 pm
Mars
Landers Preview
-
Spacecraft
names
-
Spacecraft
results
-
Pictures,
evidence of surface history
-
Surface
rock composition
-
Mars
rocks go plop plop fizz fizz
-
Weather
patterns
-
Martian
Meteorites
-
Martian
moons: Phobos and Deimos
-
Supplement:
Making a Spacecraft
Spacecraft
Names
-
Mariner
4, 6, 7 flyby, late 1960s
-
Mariner
9 orbit, 1971
-
(recall
Mariner
10 flew by Venus and Mercury)
-
Mars
2 (Soviet), 1971
-
Viking
1 and 2, 1975, 1976
-
Mars
Global Surveyor (1997-)
-
Mars
Pathfinder(1997)
-
Several
others unsuccessful
-
Mars
Polar Lander (1999,
Bad leg sensor?)
-
Mars
Climate Orbiter (1999
unit conversion)
-
Mars
Observer (1993 bad transistor?)
-
2 Soviet
(late 1980s)
Viking
Lander full-sized replica
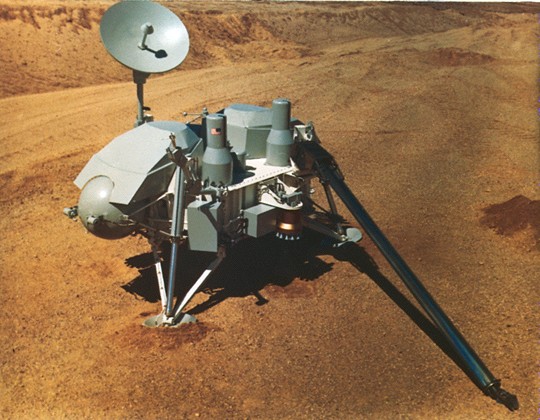

Mars
Global Surveyor

Mars
pathfinder

Spacecraft
Results
-
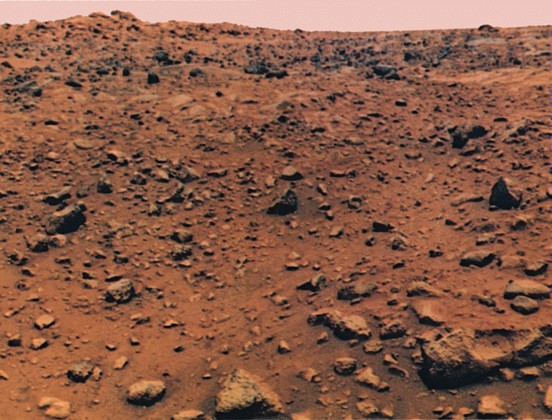
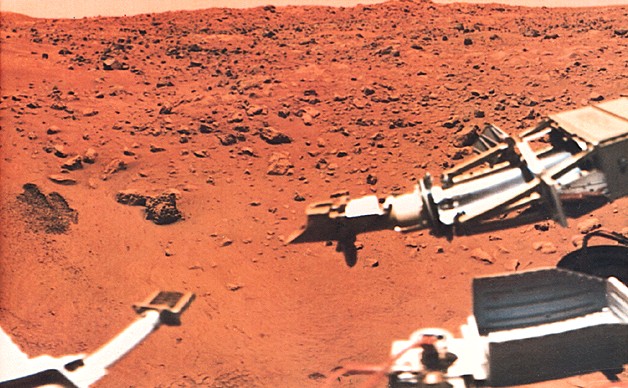
Pictures of surface
-
Visits to surface
-
pictures
-
temperatures, weather
-
chemistry
Viking Orbiter, Mars Global
surveyor
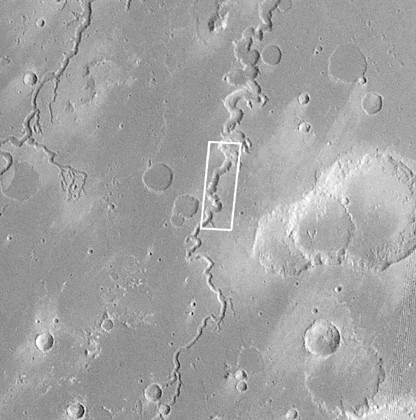

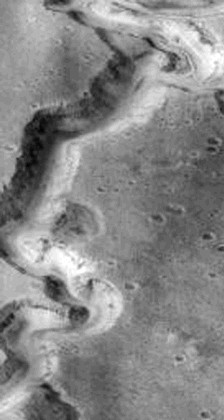
Viking 1 lander site

Viking 2 lander site

Martian
Weather
-
Martian temperatures:
-
night 180 K (-93o
C
= -135o F)
-
day 240 K (-33o
C
= -27o F)
-
Thin atmosphere doesn't old
heat in, keep sun out
-
Mars has seasons
-
Why?
-
Martian seasons so severe
part of the atmosphere freezes out!
-
Mars has an elliptical orbit
-
when it's summer in southern
hemisphere, Mars is closer to the Sun
-
Summer in the southern hemisphere
should be warmer... right?
-
Actually not! Because
of dust in the wind.
-
More direct and more intense
sunlight stirs up winds
-
Wind stirs up dust
-
Dust obscures the Sun
-
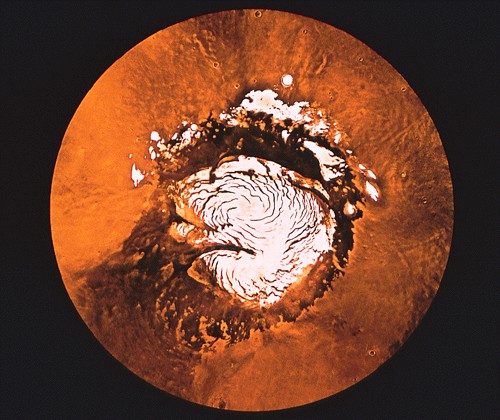
Southern ice cap is bigger
-
Wind-blown dust patterns
may also alter large-scale appearance of the Martian dark spots
-
possible reason for change
of appearance with seasons
-
Large scale student motion
experiment
-
Dust probably causes pink
Martian sky
Viking 2 site in the winter
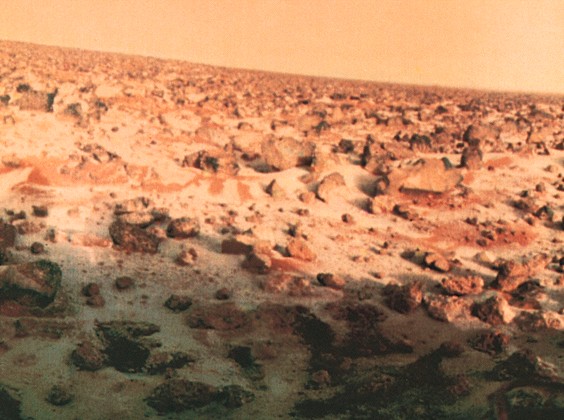

Southern ice cap
Martian
Chemistry
-
Primary
goal of Viking missions was to look for evidence of life
-
Three
sets of experiments involving Martian soil
-
Gas
exchange -- breathing
-
Labeled
release -- metabolism
-
Pyrolytic
release -- photosynthesis
-
Some
gas and water was added to the soil to stimulate growth
-
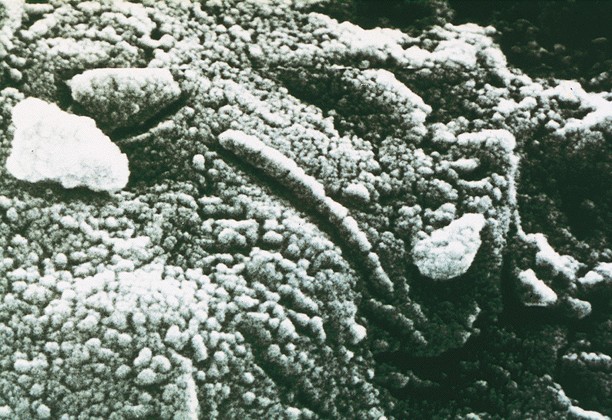
RESULTS:
Martian soil fizzes when wet
-
fizzing
a sign of strong chemical reactions
-
difficult
to detect delicate biological processes
-
soil
composition probably hostile to water-based microbial life
-
no
organic compounds detected on surface
Rock
lunch anyone?
Martian
Meteorites
-
We have discovered pieces
of other planets laying around on Earth!
-
A large impact on any planet,
moon, asteroid, sends parts flying
-
Can land anywhere on the
Earth
-
Allen Hills ice field in
Antarctica easiest place to find
-
Conveyor belt effect of ice
sheet dumps meteorites in a pile at one end
-
Chemical composition determines
where meteorite from
-
MARTIAN METEORITES MAY SHOW
FOSSILIZED MICROBES
-
small tubes
-
problems: other ways to chemically
assemble evidence
-
tubes much smaller than similar
shaped organisms on Earth
Meteorite
ALH 84001
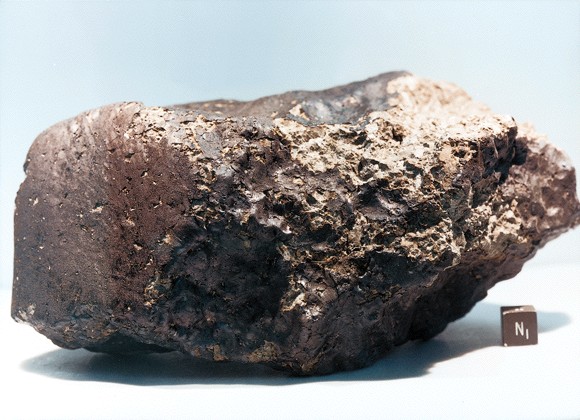

Meteorite
ALH 84001 x 100,000
Martian
Moons Phobos and Deimos
-
Fear and Panic
-
Mini-moons
-
Only 15-20 km across
-
Not enough self-gravity to
be round
-
Like Asteroids
-
Phobos orbits Mars in 7h
39m
-
Deimos orbits almost synchronously
 Phobos
and Deimos
Phobos
and Deimos

Making
a Spacecraft
-
Most
spacecraft are robotics
-
Can't
go back to fix it
-
Exception,
low Earth orbit, like Hubble Space Telescope
-
Can't
cost too much
-
Can't
do too little
-
Cutting
corners can jeopardize mission lifetime
-
Not
cutting corners jeopardizes start of mission
-
Lots
of skill in managing that fine line