Saturn
and its Moons
Printable
version
April
20, 2000
Announcements
-
IN
CLASS EVALUATIONS SOON (COME TO LECTURE)
-
Next
honors meeting April 26 OUTLINE DUE
-
Homework
#6 due next week
-
Think
about writing up observing project
-
Extra
credit project posted on web
-
Measuring
angle of sun at sunset
-
Find
West relative to landmarks
-
Use
streets, map, compass, etc
-
Measure
angle from west to your landmarks
-
to
the right (North) is plus
-
to
the left (South) is minus
-
Record
angles in graph
Saturn
and its Moons Preview
-
Saturn
overview
-
Outer
atmosphere
-
3 layers
of clouds (like Jupiter)
-
Internal
structure
-
Solved
(?) puzzles of Saturn
-
Chemical
composition
-
Excess
heat source
-
Titan
(largest moon)
-
Other
moons
-
Cassini
and Huygens probes
Saturn
Overview
-
Saturn similar in size to
Jupiter but 1/3 the mass
-
Average density is less than
water!
-
Most oblate planet (diameter
at equator greater than diameter at poles)
-
10% oblate vs 6.5% for Jupiter
-
Differential rotation
-
Poles rotate slower than
equator
-
Inside rotates slower than
equator
-
Similar to Jupiter
Saturn's
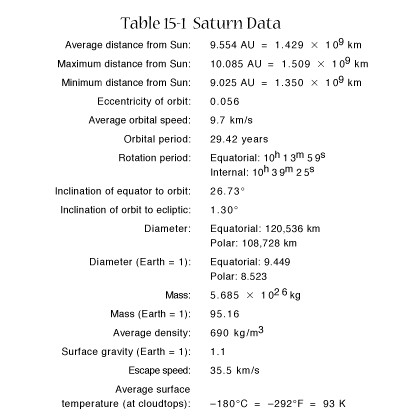
Outer Atmosphere
-
Compare
to Jupiter
-
Three
layers of clouds (like Jupiter)
-
Ammonia
(NH3)
-
Ammonium
hydrosulfide (NH4SH)
-
Water
(H2O)
-
Less
gravity on Saturn means clouds less compressed
-
Larger
haze layer between cloud
-
optical
telescopes can't see as deeply into Saturn's atmosphere
-
Saturn
less colorful
-
Saturn
has higher wind speeds see Solved Puzzles
-
No
long-lived storms like Jupiter's Great Red Spot
-
Saturn
also has belts and zones
Jupiter

Storm
on Saturn (white arrow shape)

Saturn's
Belts and Zones
Saturn's
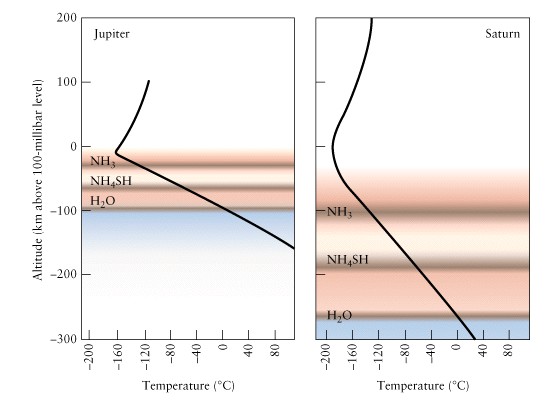
Internal Structure
-
Similar
to Jupiter
-
Rocky
core larger than Jupiter's
-
Liquid
metallic hydrogen layer smaller
-
Outer
atmosphere much thicker
-
why
more oblate and less dense
-
Where
is Saturn's magnetic field generated?
-
Liquid
metallic hydrogen layer
-
Saturn
has Aurora
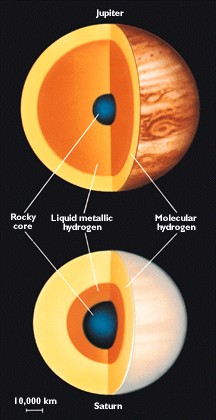
Aurora
on Saturn
Solved
(?) Puzzles of Saturn
-
Outer atmosphere composition
different from Jupiter, Sun
-
Jupiter, Sun: 80% hydrogen,
19% helium, 1% other
-
Saturn: 88% hydrogen, 11%
helium, 1% other
-
Generates 3 times more heat
than it receives from the Sun
-
Jupiter generates twice as
much
-
Why should Jupiter emit more
heat?
-
Larger
bodies retain more he
-
More
heat output contributes to higher wind speed
-
Hypothesis:
-
Saturn cold enough, dense
enough atmosphere to condense out liquid helium (like rain)
-
Falling liquid helium rain
heated lower atmosphere by friction
-
(potential energy lecture
demo)
-
heat still escaping today
Titan
-
Saturn's largest moon
-
Cold enough and big enough
to have an atmosphere
-
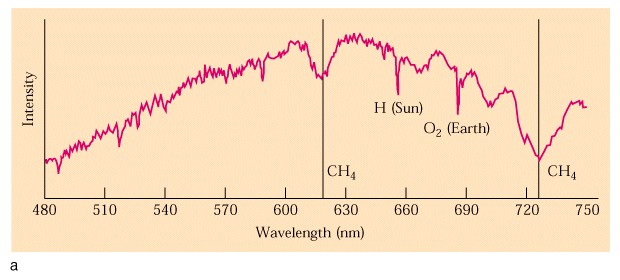
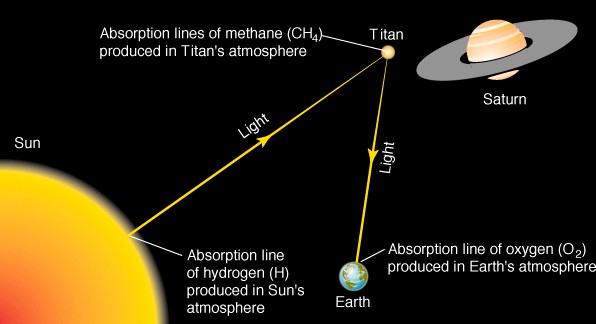
Absorption lines of CH4
(methane) seen from Earth
-
Atmosphere too thick to see
the ground in optical wavelengths!
-
Even thicker than Earth's
atmosphere!
-
No other moon with a thick
atmosphere
-
90% Nitrogen
-
what other solar system body
has a nitrogen rich atmosphere?
-
Earth!
-
Nitrogen was originally bound
in ammonia (NH3)
-
Sunlight broke up ammonia,
hydrogen floated away
-
This effect dried out which
other solar system bodies?
-
Venus
and Mars
-
Lots of methane (CH4)
-
Methane and sunlight make
hydrocarbons, in particular ethane
-
ethane may have condensed
to make rivers and lakes
-
Methane and hydrocarbons
combine to make long chain polymers (plastics)
-
Some of the longer chains
fall out of the atmosphere
-
probably gooey like melted
plastic
-
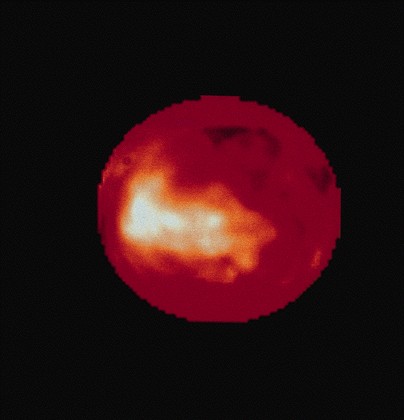
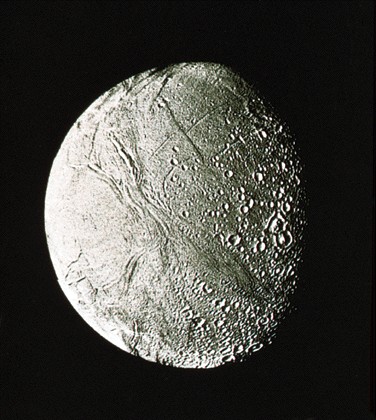
Infrared images from Hubble
Space Telescope
-
light areas may be water
and ammonia ice
-
dark areas may be hydrocarbon
lakes
Titan from Voyager (optical)
Titan from HST (infrared)

Saturn's
Other Moons
-
At least 18 moons in all
(similar to Jupiter)
-
Only Titan is really big
(between Mercury and Mars)
-
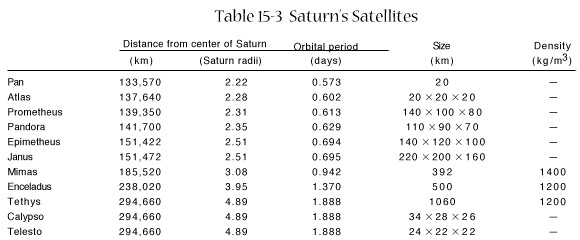
6 moderate sized moons
-
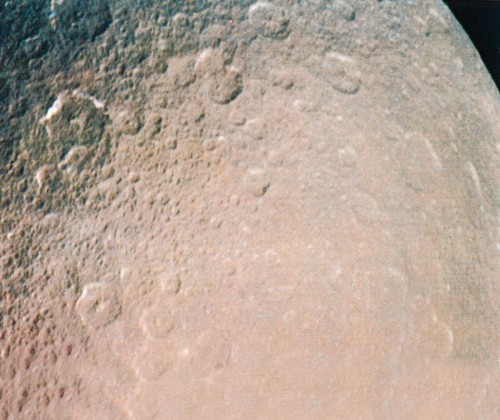
Mimas
-
Enceladus
-
Recent geologic activity
-
Source of heat mystery
-
More reflective than new
snow
-
Tethys
-
Dione
-
Leading hemisphere cratered
-
Trailing hemisphere has weird
wisps
-
Rhea
-
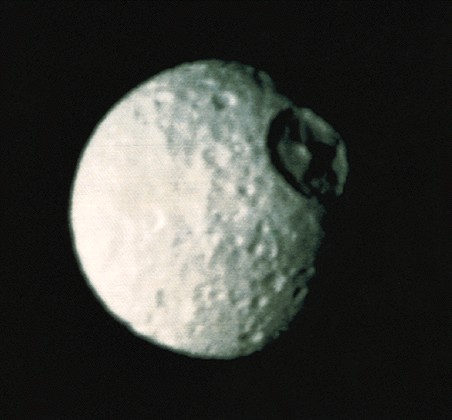
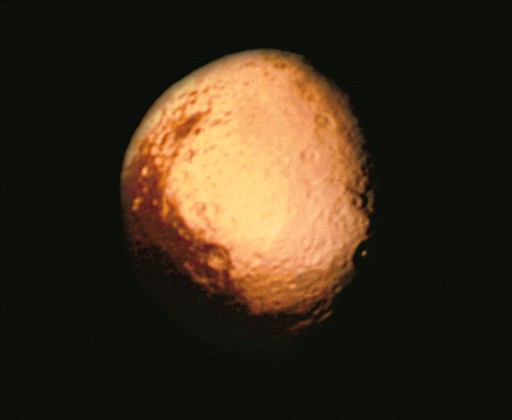
Iapetus
-
Leading hemisphere very dark
-
Material may be from Phoebe
-
trailing light
-
Synchronous rotation, prograde
-
Average densities 1200-1400
kg/m3 (ice)
-
Several rock or ice fragments
-
Pan (makes Encke Gap)
-
Prometheus and Pandora (F-ring
shepherds)
-
...
-
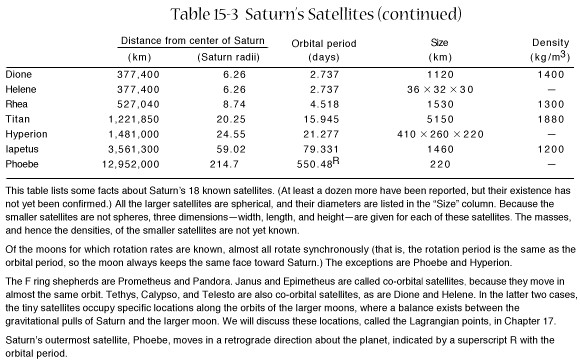
Mimas

Enceladus
Tethys MPEG
movie of Tethys

Dione trailing hemisphere
Rhea

Iapetus

Cassini
and
Huygens
-
Cassini
is a space probe that will orbit Saturn
-
Huygens
currently attached to Cassini will fall into Titan's atmosphere
-
Why
doesn't Cassini have any solar panels?
-
Too
far from Sun
-
Nuclear
powered
-
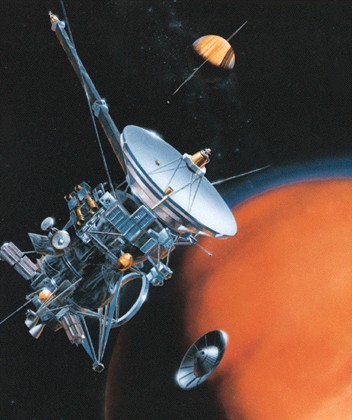
Saturn
and its Moons Summary
-
Saturn
overview
-
Outer
atmosphere
-
3 layers
of clouds (like Jupiter)
-
Internal
structure
-
Solved
(?) puzzles of Saturn
-
Chemical
composition
-
Excess
heat source
-
Titan
(largest moon)
-
Other
moons
-
Cassini
and Huygens probes




















